Recently, there has been a dramatic increase in the use of XML data to deliver information over the Web. In particular, personal Weblogs, news Web sites, and discussion forums. Now delivering up-to-date postings to their subscribers using the Feed Reader protocol. To help users access new content in this RSS domain. A number of aggregation services and blog search engines have appeared recently and are gaining popularity. Clearly, having a central access point makes. It significantly simpler to discover and access new content from a large number of diverse sources.
In this project, we investigate one of the important challenges in building an effective aggregator. How can we minimize the delay between the publication of new content at a source and its appearance at the aggregator? This problem is similar to the index refresh problem for Web search engines. But two important properties of the information in the RSS domain make this problem unique and interesting. Eventually, the scope identifies the software product to be produced, the capabilities, application, relevant objects etc.
The information in the RSS domain is often time-sensitive. Most new content is related to current world events, so its value and significance deteriorate rapidly as time passes. An effective aggregator, therefore, has to retrieve new content quickly and make it available to its users’ close to real-time. This requirement is in contrast to general Web search engines where the temporal requirement is not as strict. For example, it is often acceptable to index a new Web page within month. Its creation for the majority of Web pages. For general search engines, users mainly focus on the quality of the returned pages and largely ignore what is not returned.
Diagrams Needed for this Project are:
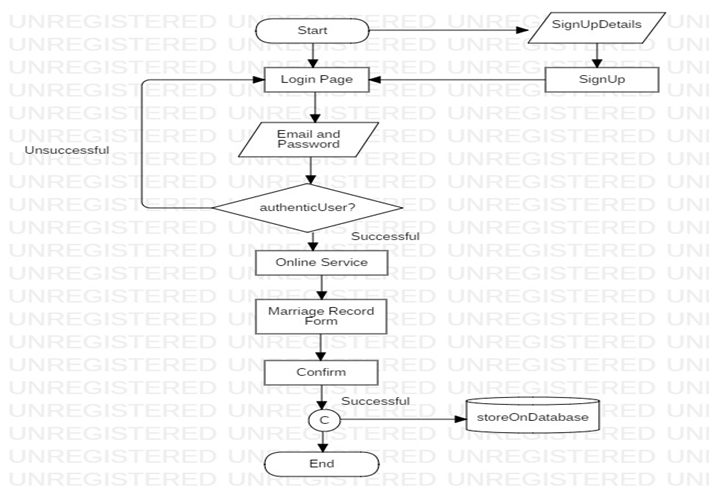
- Data Flow
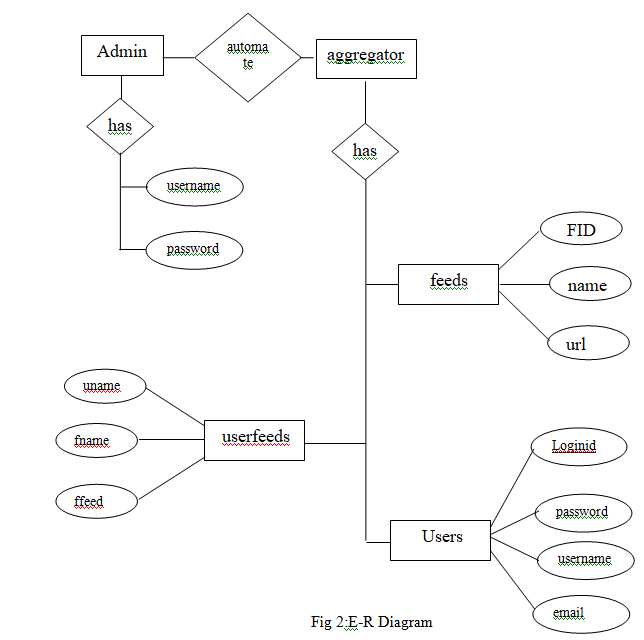
- ER Diagram
- Schema Diagram
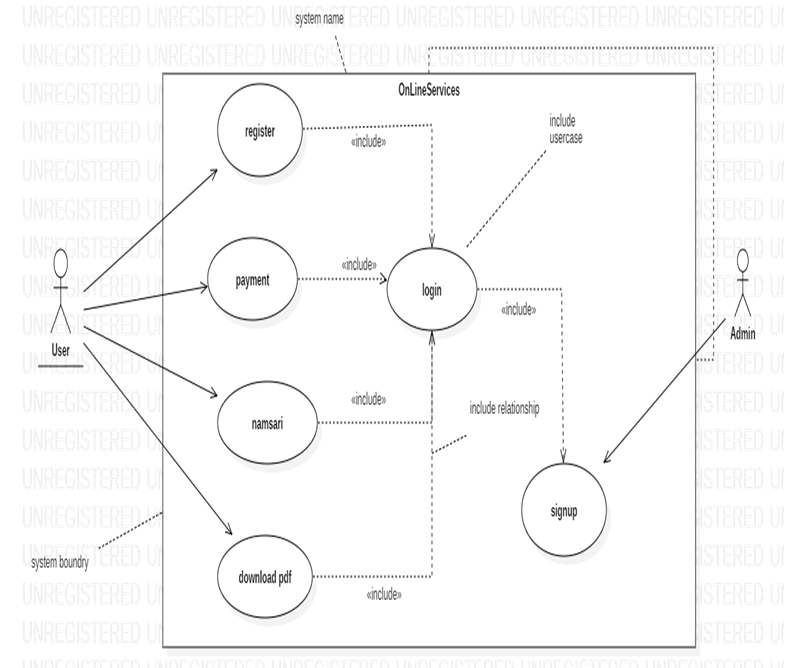
- Use Case Diagram