When you write codes, most of the times you want to perform various actions for different decisions in your programs.
We have the following conditional statements :
- if = defines block of code to be executed, if specified condition is true
- else = defines a block of code to be executed, if same condition is false
- else if = defines a new condition to test, if first condition is false
- switch = defines many alternative blocks of code to be executed
If Statement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Displays "Good day" if hour is less than 17:00:</p>
<p id="ex">Good Evening</p>
<script>
if (new Date().getHours() < 17) {
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = "Good day";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :
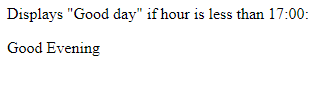
Else Statement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Click the button to display a time-based greeting:</p>
<button onclick="myFunction()">Click Here</button>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
function myFunction() {
var hour = new Date().getHours();
var greeting;
if (hour < 17) {
greeting = "Good day";
} else {
greeting = "Good evening";
}
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = greeting;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

Else If Statement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Click the button to display a time-based greeting:</p>
<button onclick="myFunction()">Click Here</button>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
function myFunction() {
var greeting;
var time = new Date().getHours();
if (time < 10) {
greeting = "Good morning";
} else if (time < 20) {
greeting = "Good day";
} else {
greeting = "Good evening";
}
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = greeting;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :