It is the set of the rules how programs are constructed.
JS Programs :
A computer program is list of “instructions” to be “executed” by computer. These program instructions are called statements in programming language.
JS Statements are separated by semicolons;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>JS Statements</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
var x, y, z;
x = 2;
y = 8;
z = x + y;
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = z;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

JS Statement :
It is formed of Values, Operators, Keywords, Comments, and expressions.
JS Values :
It defines two types of values:- Variable values and Fixed Values. Variable values are called variables and fixed values are known Literals.
JS Variables :
To store data values variables are used. To declare variables the car keyword is used by Javascript. To allow values to variables, an equal (=) sign is used.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>JS Variables</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
var x; //x is defined as a variable. Then, x is assigned the value of 6
x = 5;
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = x;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Ouput :

JS Literals :
The important rules for writing fixed values are: numbers are written with or without decimals.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>JS Numbers</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = 10.50; //Numbers can be written with or without decimals
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :
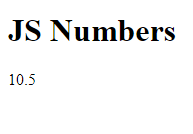
String are Text and it can be written within single or double quotations.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>JS Strings</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = 'Code Projects';
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

JS Operators :
( + – * / ) Arithmetic Operators are used to compute values.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>JS Operators</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = (2 + 2) * 10;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

To assign values (=) assignment operator is used.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>Assigning Values</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
var x, y;
x = 8;
y = 4;
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = x - y;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

JS Expressions :
Expression is a combination of variables, values & operators, which computes to a value.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>JS Expressions</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = 5 * 5;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :
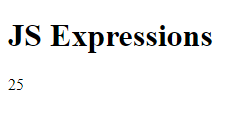
The values can be numbers and strings.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>JS Expressions</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = "Code" + " " + "Projects";
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

JS Keywords :
Keywords are used to identify actions to be performed. var keyword tells browser to create variables.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>JS Keywords</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
var x, y;
x = 2 + 2;
y = x * 10;
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = y;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

JS Comments :
Codes after double slashes ( // ) or between ( /* and */ ) is known comment and it will not be executed.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>Comments are not executed</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
var x;
x = 5; // x = 6; I will not be executed
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = x;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

JS Identifiers :
Identifiers are used to name variables (and keywords, and functions, and labels). First character must be a letter, or a dollar sign ($) or an underscore (_).
JS is Case Sensitive :
Variables Code and code, are two different variables.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>Case Sensitive</h1>
<p id="ex"></p>
<script>
var projects, Projects;
lastName = "Code";
lastname = "Code";
document.getElementById("ex").innerHTML = lastName;
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output :

JS and Camel Case :
Hyphens: //this is not allowed in js.
first-name, last-name, cr-card.
Underscore:
first_name, last_name, cr_card.
Upper Camel Case:
FirstName, LastName, CreditCard.
Lower Camel Case:
firstName, lastName, creditCard.
JS Character Set:
JS uses unicode character set and it covers all characters, symbols & punctuations in the world.